PJM’s Capacity Auction: The Real Story
Fossil fuel un-reliability and PJM’s failure to speedily connect new clean resources to the grid are to blame for the 2025/26 auction price spike.
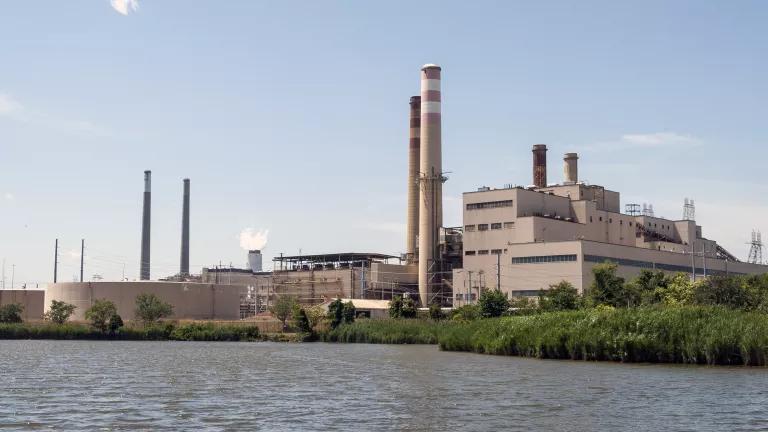

View of the Herbert A. Wagner Coal Generating Station in Maryland. Fossil fuel plants like Wagner caused the price spike in PJM's latest auction.
On July 30, PJM announced the results of its capacity auction for 2025-2026, which showed total costs of nearly $14.7 billion, compared to last year’s $2.2 billion. There are two major causes for blame: fossil fuel un-reliability and PJM’s failure to speedily connect thousands of megawatts of wind, solar, and storage to the grid. This was foreseeable and preventable, and PJM’s failure to allow for new clean energy to come online and plan for more transmission has forced the bill onto ratepayers.
In this blog, we’ll break down what happened, and show that solutions are within reach.
What happened?
PJM’s capacity market is set up to ensure that there is enough electricity to meet demand on the hottest and coldest days of the year. Capacity auctions, which happen annually, occur when power plants are paid to commit to be available, or customers are paid to conserve during emergencies.
For years, PJM has over-relied on fossil fuel power plants, even while affordable new power sources are coming online. Gas plants are prone to fail during extreme weather, such as winter storm Elliott in 2022 – when we need them the most. Since PJM did not account for fossil resource weaknesses in its previous capacity market auctions, customers paid for these plants as if they were reliable. That’s like buying a house at full price only to realize the foundation is crumbling. It now turns out that the repairs are quite expensive.
Last year, PJM took the first step in remedying this problem by changing the way all resources are evaluated for reliability, resulting in a more accurate process known as “marginal capacity accreditation.” According to S&P Global, the result was that roughly 26 gigawatts (GW) of gas and coal resources were shown to be unreliable, and thus could no longer claim to benefit PJM at their assumed full output during all weather conditions.
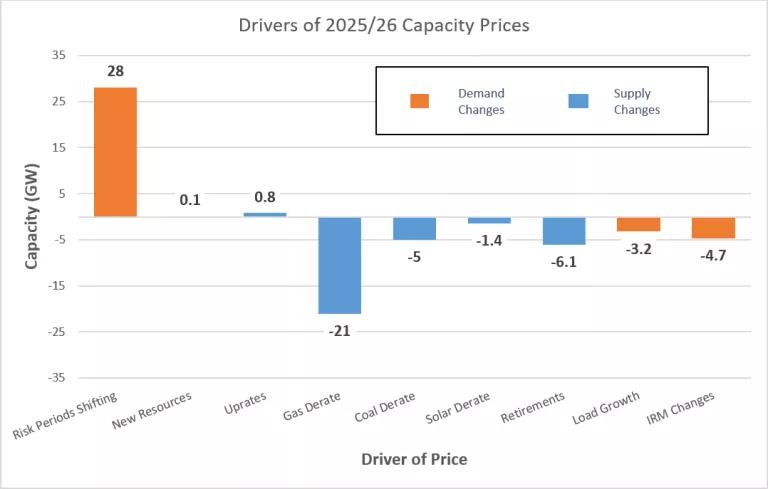
This chart shows the drivers for the change in PJM’s capacity prices between the last auction (for the 2024-5 year) and the most recent auction (2025-6). Both supply and demand changes drove the price increase. Negative values indicate reductions in capacity in PJM’s system, while positive values indicate additional available capacity. Market changes to better evaluate the reliability of all resources caused the shift in risk periods and resulting additional capacity (far left orange bar), the gas derates, the coal derates, the solar derates, and the changes to the Installed Reserve Margin (IRM). We can see that the reduction in gas capacity is the largest driver for the “tightening” of PJM’s system. Retirements and load growth, while significant, contributed less to the overall price. Only 110 MW (0.1 GW) of new resources came online to help provide capacity; the low number is due mostly to slow interconnection queues.
NRDC
As with most markets, when supply falls, prices rise. With 26 GW of gas and coal resources now deemed to be unreliable and therefore not counted in its capacity market, the price of capacity in PJM spiked. Affordability, but not reliability, is now at risk.
We need not have come to this place. Why? There are over 286 GW of new resources waiting to come online in the interconnection queue. That is far more than the 135 GW of resources that cleared in the PJM auction. Even a fraction of these queued resources could significantly improve reliability and affordability if they were able to come online.
Unfortunately, PJM has slow-walked interconnection reforms to connect these resources to the grid. This sticker shock is a direct result of delays in getting new energy online, together with the transmission to support it. Many of these resources would have absorbed and buffered the price increases by increasing supply.
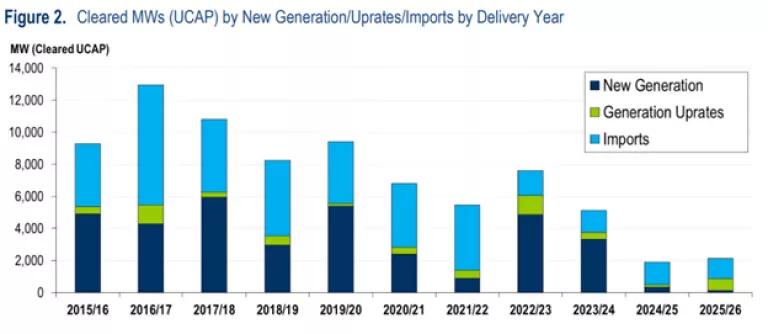
Fewer new resources and imports participated in the 2025/26 auction than ever before, showing a clear downward trend.
PJM Interconnection, “2025/2026 Base Residual Auction Report,” July 30, 2024.
This doesn’t mean we need more gas – on the contrary, it shows that fossil fuels are expensive and unreliable, and a diverse resource mix will benefit the region far into the future. These high prices are sending a signal to build, and PJM shouldn’t stand in the way of progress. Instead, PJM seems more interested in keeping aging and expensive fossil plants alive, such as Brandon Shores in Maryland, rather than expediting the interconnection of new resources to the PJM power system.
What about retirements and load growth?
Around 6 GW of fossil plants retired since the last auction. The fossil lobby will say this is due to draconian regulations that are forcing power plants to retire before their time, but the truth is that most of these plants are no longer economically viable. Most of the retiring resources are decades-old coal plants, built in the 1960s, and some are facing bankruptcy. Lower-cost, reliable clean energy can replace even more of them, but only if they can get online – which requires PJM to accelerate the interconnection process.
Projected load growth of 3.2 GW further strained the system, which is a 2.2% increase over the last planning year. Planning for load growth and retirements is important, but the principal driver of the capacity market price increase was PJM derating the gas plants to reflect their lower reliability value. The gas and coal derating (26 GW) was nearly three times as much as the combination of retirements and load growth.
How can we fix this?
PJM needs new resources, and quickly. The good news is that there are currently 268 GW of new resources patiently waiting to come online in PJM, and 95% of those resources are clean. Adding even a fraction of this capacity would dramatically reduce prices.
To estimate the potential cost savings, we constructed a “no backlog” scenario in which 30% of renewable projects that have been stuck in the queue for at least five years were instead assumed to be operational and had bid into the capacity market. The capacity value of these new resources would amount to an additional 7 GW of supply in the most recent auction. Adding just 7 GW of new entry could have lowered the market clearing price from $269.92/MW-day to as low as $98, or by as much as 63%. PJM delays in implementing interconnection queue reforms have effectively blocked new entry, driving up capacity costs and failing to mitigate the price impact for consumers.
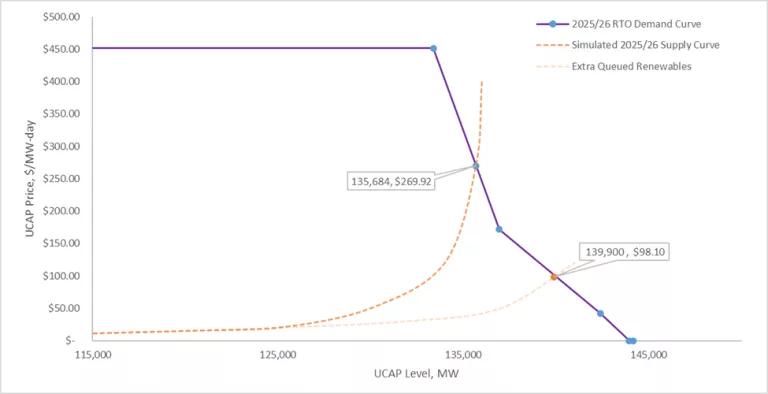
The 2025/2026 BRA cleared 135 GW of capacity at a price of $269.92/MW-day. This graph reconstructs the supply curve that produced actual clearing results compared to a “no backlog” supply scenario that includes 7 GW of capacity value from new renewable entry. Additional capacity from backlogged resources could have lowered the market clearing price to under $100/MW-day.
NRDC
There are three things PJM can do to bring down prices.
First, PJM must comply with FERC’s interconnection Order 2023 as soon as possible. PJM has refused to comply with the order so far, but after this auction it should be able to see the urgency of meaningful interconnection reform and comply as soon as possible.
Second, the region needs new, well-planned transmission. A new report from Americans for a Clean Energy Grid shows that the rate of building new transmission lines is at an all-time low. If PJM’s transmission planning had a grade, it would get a D-. FERC Order 1920 charts a path toward the grid of the future and requires that RTOs, like PJM, create a process to plan for new transmission that provides regional benefits. Doing so will help to add many gigawatts of clean capacity to the power grid.
Third, PJM should examine market barriers that could be quickly fixed before the next capacity market auction in December. For example, customers in PJM currently pay hundreds of millions of dollars to keep at least two coal plants on-line for reliability reasons. Remarkably, neither of these plants bid into the capacity market this year, significantly tightening the supply in the region. PJM should require these plants, and another other future plants in such circumstances, to bid into the capacity market. If they did, customers in Maryland would have saved up to $18 per month, and the PJM region as a whole would have saved $5 billion.
PJM has the tools in its toolbox to bring down prices and ensure a reliable, clean supply of electricity for years to come. If it acts now, these price increases can just be a bump in the road to a more affordable, resilient grid.